Diabetes and Oral Health: Your Ultimate Guide for Healthy Smile!
Have you ever thought about how diabetes might affect your oral health? It’s a surprising but essential connection to understand. Diabetes doesn’t just impact blood sugar; it can also lead to various oral health issues, from gum disease to tooth decay. And here’s the twist: these oral health problems can, in turn, make managing your blood sugar levels more difficult.
In this guide, we’ll dive into the link between diabetes and dental health, explore why it matters, and share some practical tips to keep your teeth and gums in top shape. Whether you’re living with diabetes or know someone who is, let’s look at how to protect your smile and overall health.
Understanding the Link Between Diabetes and Oral Health
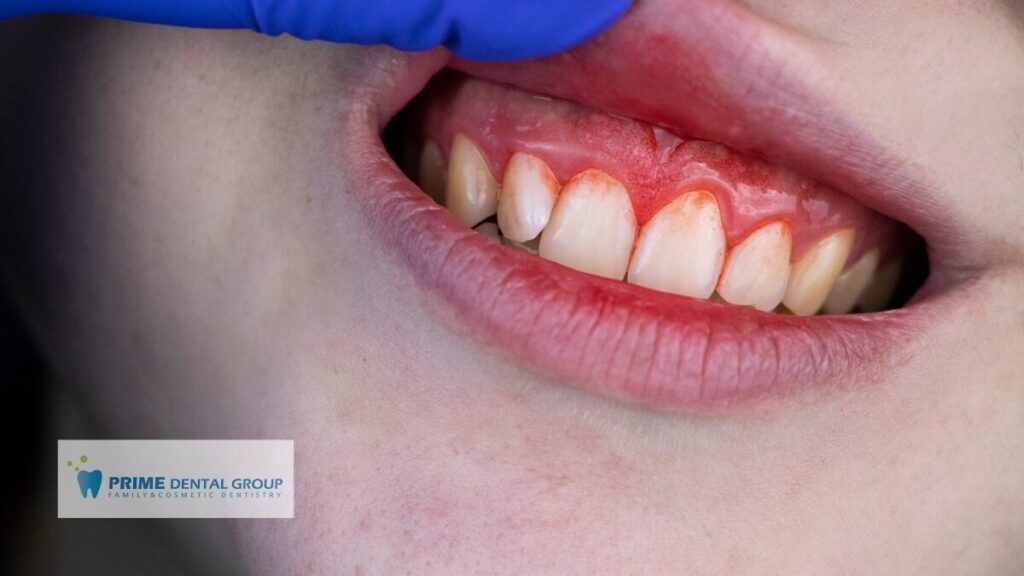
So, what exactly is the connection between diabetes and your mouth? In simple terms, high blood sugar levels can wreak havoc on your gums and teeth. When your blood sugar is high, more sugar is present in your saliva. This creates a breeding ground for harmful bacteria in your mouth, leading to infections and inflammation in the gums, a condition known as periodontal disease.
In fact, periodontal (or gum) disease is more common and often more severe in people with diabetes. It starts with red, swollen gums (gingivitis) and, if left untreated, can progress to periodontitis, which is a more serious condition that affects the bone supporting your teeth. Periodontitis can eventually lead to tooth loss—and even make managing diabetes harder. The reason? The inflammation from gum disease can elevate blood sugar levels, creating a cycle that’s challenging to break.
But that’s not all. Diabetes can also reduce saliva production, leading to dry mouth, which increases the risk of tooth decay. Saliva is our natural mouth cleanser, washing away food particles and bacteria. Without enough saliva, the risk of cavities goes up.
Common Dental Issues Diabetics Should Watch For
People with diabetes are more prone to specific oral health issues. Here are a few common ones:
- Gum Disease (Periodontitis): People with diabetes have a higher risk of developing gum disease due to increased blood sugar levels. Gum disease can lead to tooth loss and make it harder to control blood sugar, creating a vicious cycle.
- Tooth Decay: High blood sugar means higher sugar levels in your saliva, which fuels bacteria that cause tooth decay. Diabetics are at a greater risk of cavities because of this.
- Dry Mouth: Diabetes can cause reduced saliva flow, leading to dry mouth. This increases the risk of cavities, as saliva is essential for washing away food particles and neutralizing acids in the mouth.
- Oral Infections (Thrush): Fungal infections, like thrush, are more common in people with diabetes. This is due to a higher glucose level in saliva and a weakened immune system, which makes it easier for fungal infections to thrive.
- Slow Healing: High blood sugar can also slow down your body’s healing processes. This means that cuts or sores in the mouth may take longer to heal, increasing the risk of infection.
Real-World Example: Imagine two people, one with diabetes and one without, both with mild gum inflammation. For the person with diabetes, that inflammation can quickly escalate due to their body’s reduced ability to fight infections, and it could even cause a spike in blood sugar. This example shows just how interconnected oral health and diabetes are.
Actionable Tips to Protect Your Smile if You Have Diabetes
Managing your dental health as someone with diabetes is a bit like a team sport. It requires effort, consistency, and often some extra support from your dental and medical teams. Here are some easy-to-follow tips to help you keep your mouth healthy.
1. Wear Your Retainer (If You’ve Had Orthodontic Treatment)
If you’ve had braces or aligners, wearing your retainer as directed by your orthodontist is essential to keep your teeth from shifting. Teeth can sometimes move back to their original position after orthodontic treatment, especially if gum disease is present.
2. Maintain Good Oral Hygiene
Keeping up with brushing and flossing is vital, especially if you have diabetes. Brush at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and floss daily. This routine removes plaque and bacteria that can lead to gum disease and cavities. Think of brushing and flossing as your first line of defense!
3. Schedule Regular Dental Visits
Regular check-ups are critical. During these visits, your dentist can catch early signs of gum disease, tooth decay, or other issues that might be exacerbated by diabetes. Early intervention can help prevent these problems from spiraling out of control.
4. Watch Your Diet
What you eat affects not just your blood sugar but also your oral health. Try to avoid sticky, sugary, or acidic foods that can harm your teeth. Instead, opt for a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Also, drink plenty of water to help rinse away sugars and acids from your teeth.
5. Consider a Mouthguard for Sports
If you or your child participates in sports, a mouthguard is a smart investment. A mouthguard protects your teeth from injury and is especially useful if you’re wearing braces or have recently completed orthodontic treatment.
The Importance of Blood Sugar Control for Oral Health
Keeping your blood sugar within a healthy range is not only essential for overall health but also crucial for your teeth and gums. When blood sugar levels are well-managed, there’s less sugar in your saliva to feed harmful bacteria, reducing the risk of gum disease and cavities.
By working with your healthcare team to keep your blood sugar steady, you’ll make a positive impact on your oral health. This team approach, involving both your doctor and your dentist, is key to managing diabetes and preventing complications.
When to Seek Immediate Care
Diabetes can make you more prone to dental emergencies, so it’s essential to recognize warning signs. If you experience severe tooth pain, swelling, excessive bleeding, or an infection in your mouth, don’t ignore it. These could be signs of a serious problem that requires immediate attention.
Delaying care can lead to complications, especially for diabetics, who may have slower healing times and a higher risk of infection. If you’re ever unsure, it’s best to contact your dentist right away for advice.
Conclusion
Oral health and diabetes are more connected than many people realize. When blood sugar levels are high, they create a perfect storm for gum disease, tooth decay, and other oral health issues. The good news is that with proper care and a few adjustments to your daily routine, you can protect your smile and improve your diabetes management.
Remember, a healthy smile starts with regular check-ups, proper oral hygiene, and controlled blood sugar levels. And if you ever have concerns about your dental health or how diabetes might be affecting it, reach out to your dental team—they’re here to help!
Take charge of your health by working closely with your dentist and healthcare provider—it can make all the difference in managing both your diabetes and oral health. Don’t wait! Start your journey toward a healthier, happier smile today. Call Bellevue Prime Dental Group at (425) 605-3575 or Lynnwood Prime Dental Group at (425) 251-0707 to schedule your appointment!
References
- Diabetes, Gum Disease, & Other Dental Problems – NIDDK – https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/preventing-problems/gum-disease-dental-problems
- Promoting Oral Health – https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/hcp/clinical-guidance/how-to-promote-oral-health-for-people-with-diabetes.html
- Diabetes – https://www.mouthhealthy.org/all-topics-a-z/diabetes


