Gum Disease: Prevention and Treatment Guide for a Healthier Smile
Gum disease is one of the most common oral health issues among adults, yet many people don’t realize they have it until it becomes serious. Did you know that nearly half of American adults over 30 have some form of gum disease? The good news is that with the right care and habits, you can prevent gum disease and keep your smile healthy.
In this guide, we’ll break down what gum disease is, its causes, how to prevent it, and what treatment options are available. Let’s dive in!
What is Gum Disease?
Gum disease (also known as periodontal disease) is an infection of the tissues that support your teeth. It usually starts with plaque—a sticky film of bacteria that forms on your teeth. If plaque isn’t removed with daily brushing and flossing, it hardens into tartar, which can only be removed by a dentist.
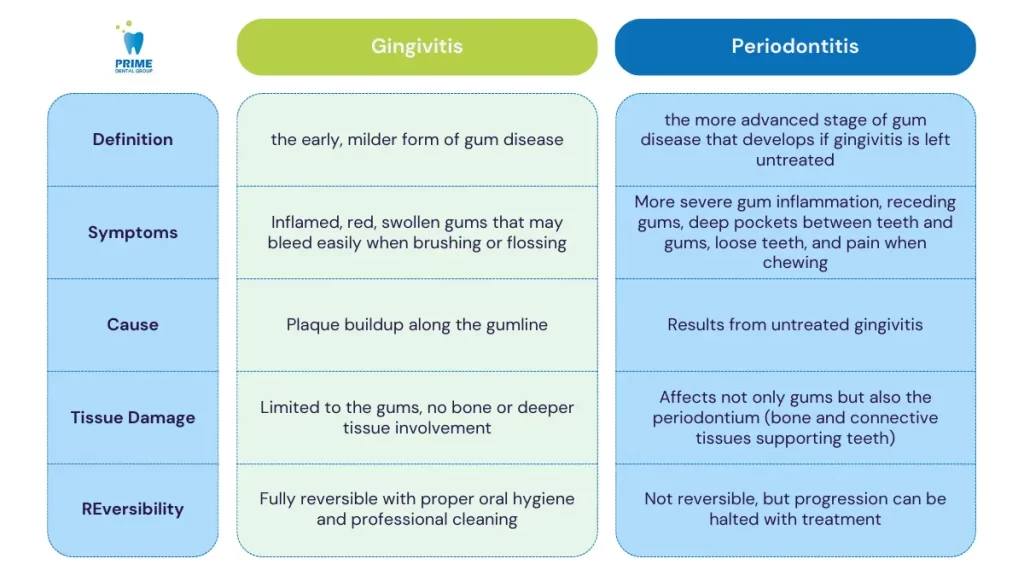
There are two main stages of gum disease:
- Gingivitis (Early Stage) – This is the mildest form of gum disease, causing redness, swelling, and bleeding gums. The good news? It’s reversible with good oral hygiene and professional cleanings.
- Periodontitis (Advanced Stage) – If gingivitis is left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis. This stage leads to gum recession, bone loss, and even tooth loss. Treatment at this stage requires professional intervention.
What Causes Gum Disease?
Gum disease doesn’t happen overnight. Several factors can increase your risk:
1. Poor Oral Hygiene
Not brushing and flossing regularly allows plaque and tartar to build up, leading to gum infections.
2. Smoking and Tobacco Use
Smokers are 2-3 times more likely to develop gum disease than non-smokers. Smoking weakens the immune system, making it harder for your gums to fight infections.
3. Hormonal Changes
Pregnancy, menopause, and even puberty can make gums more sensitive and prone to inflammation.
4. Health Conditions Like Diabetes
People with diabetes are at a higher risk because high blood sugar levels can make infections, including gum disease, worse.
5. Genetics
If your family has a history of gum disease, you may be more prone to developing it as well.
6. Medications
Certain drugs, such as antidepressants and high blood pressure medications, can reduce saliva flow, increasing the risk of gum disease.
Signs and Symptoms of Gum Disease
The sooner you recognize gum disease, the easier it is to treat. Look out for these warning signs:
✅ Red, swollen, or tender gums
✅ Bleeding gums when brushing or flossing
✅ Persistent bad breath (halitosis)
✅ Receding gums (your teeth look longer than before)
✅ Loose or shifting teeth
✅ Pain when chewing
If you notice any of these symptoms, schedule a dental check-up as soon as possible!
How to Prevent Gum Disease
Prevention is key! Follow these simple tips to keep your gums healthy:

1. Brush Twice a Day
Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste to gently clean your teeth and gums. Don’t forget to brush your tongue—it harbors bacteria too!
2. Floss Daily
Flossing removes plaque from between teeth and under the gumline, where your toothbrush can’t reach.
3. Use an Antimicrobial Mouthwash
Mouthwash helps reduce bacteria and keeps your breath fresh. Look for one with fluoride for extra protection.
4. Eat a Healthy Diet
Limit sugary and processed foods that feed harmful bacteria. Instead, eat foods rich in vitamins C and D, such as oranges, leafy greens, and dairy products, to keep your gums strong.
5. Quit Smoking
If you smoke, quitting is one of the best things you can do for your gum health (and overall health!).
6. Visit Your Dentist Regularly
Regular cleanings and check-ups help catch gum disease early. Dentists can remove tartar buildup that brushing and flossing can’t handle.
Treatment Options for Gum Disease
If you already have gum disease, don’t worry—there are effective treatments available!
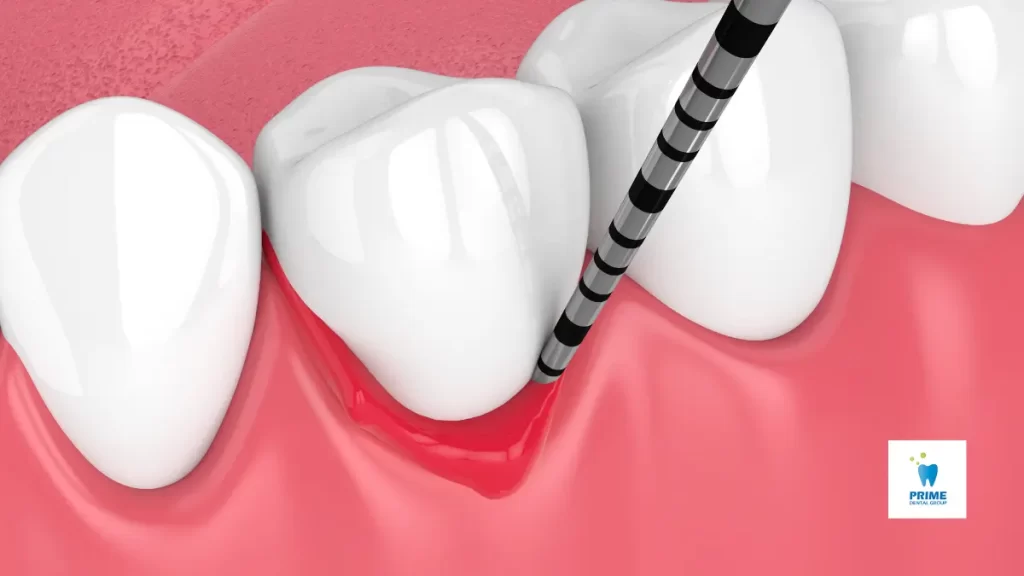
1. Deep Cleaning (Scaling and Root Planing)
This non-surgical treatment removes plaque and tartar from below the gumline and smooths the root surfaces to prevent bacteria from sticking.
2. Antibiotic Therapy
In some cases, dentists prescribe antibacterial mouth rinses or oral antibiotics to fight the infection.
3. Laser Therapy
Laser treatment can help remove infected gum tissue and encourage healing, with less discomfort than traditional surgery.
4. Gum Surgery (For Advanced Cases)
If gum disease has caused severe damage, procedures like flap surgery or gum grafts can restore lost gum tissue and prevent further bone loss.
Why Treating Gum Disease Matters
Ignoring gum disease can lead to serious health problems beyond your mouth. Research has linked gum disease to:
🫀 Heart Disease – Gum infections can contribute to inflammation in the body, increasing the risk of heart disease.
🧠 Alzheimer’s Disease – Studies show that bacteria from gum disease can travel to the brain and contribute to cognitive decline.
📉 Diabetes Complications – Uncontrolled gum infections can make diabetes harder to manage.
Taking care of your gums isn’t just about your smile—it’s about your whole-body health!
Take Action for Your Gum Health Today!
Gum disease is preventable and treatable, but early action is key. By maintaining good oral hygiene, visiting your dentist regularly, and making healthy lifestyle choices, you can keep your gums strong and your smile bright.
If you’re experiencing any signs of gum disease or need a professional cleaning, we’re here to help! Contact Bellevue Prime Dental Group at (425) 605-3575 or Lynnwood Prime Dental Group at (425) 251-0707 to schedule an appointment today.
Your smile deserves the best care—let’s keep it healthy together!
FAQs About Gum Disease
1. Can gum disease be reversed?
Yes! Gingivitis (the early stage) can be reversed with good oral hygiene and professional dental cleanings. However, advanced periodontitis requires ongoing treatment to manage.
2. How often should I see a dentist to prevent gum disease?
It’s best to see a dentist every six months for a check-up and professional cleaning. If you have gum disease, your dentist may recommend more frequent visits.
3. Does gum disease cause bad breath?
Yes, persistent bad breath can be a sign of gum disease. The bacteria in plaque and tartar release foul-smelling toxins that lead to bad breath.
4. Can I get gum disease even if I brush my teeth daily?
Yes—if you don’t floss, avoid dental check-ups, or have risk factors like smoking or diabetes, you may still develop gum disease. Brushing alone isn’t enough—flossing and regular dental cleanings are essential!
5. Is gum disease painful?
Early-stage gum disease (gingivitis) isn’t usually painful, but as it progresses to periodontitis, you may experience pain, gum recession, and loose teeth.
By taking simple steps today, you can prevent gum disease and protect your beautiful smile for years to come. Book your dental visit today—your gums will thank you! 😊




